Introduction
You can’t diet forever, nor should you. In fact, even if you need to lose 100+ pounds, taking breaks from dieting is an important part of the weight loss process. This NutriWiki article will break down the details about tell you how to take a diet break.
Summary
A diet break is, as the name indicates, a controlled break from dieting where calories (with an emphasis on carbohydrates) are brought to estimated caloric maintenance for a period of time that goes from 10 to 14 days (or maybe longer), in order to reverse metabolic adaptations that occur when dieting and improve long term adherence.
Discussion
Diet breaks can be scheduled on a per needed basis, with them occurring as often as every 2 weeks, or as sparse as every 6-12 months, depending on the individual.
One study found that over a 16 week period, people who took a one week diet break every 2 weeks saw greater weight loss results over the course of the study than people who dieted the entire time [1].
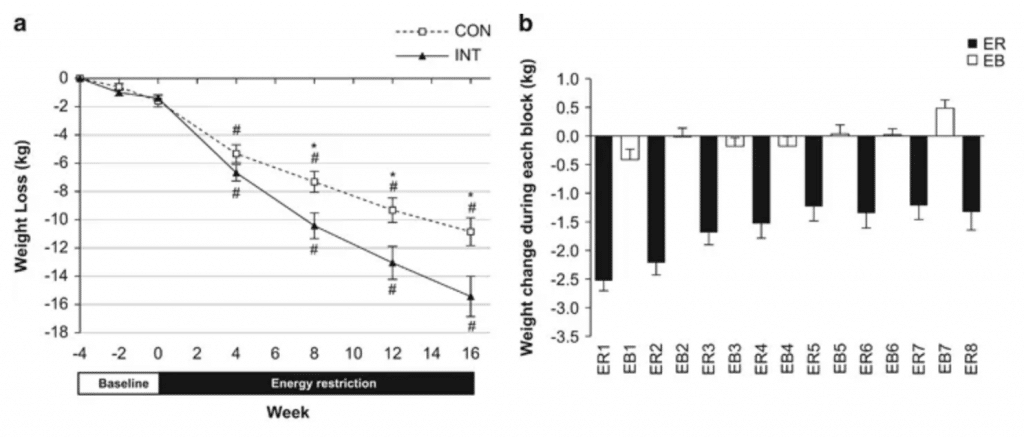
While most people might benefit from diet breaks, there are a few things to consider:
1. Your weight might go up due to the increased amount of food, replenishment of muscle glycogen stores, water weight. None or maybe just a little bit of the weight gain is going to be stored fat, which is going to come off once getting back into a caloric deficit anyway.
2. Your weight could stabilize and stay there where it is.
3. You could experience a big drop in weight on the first days thanks to the increased carbohydrates that decrease cortisol levels, causing water weight loss [2].
Another potentially important aspect about diet breaks is the effect they may have on hormones. The adipose tissue (fat) produces a hormone called Leptin, which tells your brain how much you’re eating and what your bodyfat is, regulating your caloric expenditure. When dieting, body fat is reduced, therefore less Leptin is produced. This decreases overall energy expenditure, NEAT, making you burn less calories & plateau due to the decreased energy output.
More Leptin = more energy & more bodyfat.
Less Leptin = less energy & less bodyfat.
The purpose of a diet break is to reverse many of the features of metabolic downregulation that occur with dieting by increasing total calories and especially carbohydrates (which is the only macronutrient that has a positive impact on it), increase energy expenditure, and get back to dieting with a recovered hormonal profile. It also is an effective tool for managing the psychological aspects of dieting.
