Weight loss surgery, also known as bariatric surgery, has emerged as a powerful option for individuals struggling with severe obesity.
This surgical intervention goes beyond conventional weight loss methods, aiming to address not only physical changes but also the hormonal and psychological factors that contribute to obesity.
In this article, we will delve into the world of weight loss surgery, exploring its different types, short-term results, long-term results, hormonal implications, and the vital role of lifestyle changes in ensuring long-term success.
Jump to a Topic
What is Weight Loss Surgery?
Weight loss surgery encompasses a range of surgical procedures designed to modify the gastrointestinal tract, ultimately leading to reduced food intake, enhanced satiety, and significant weight loss. These procedures are typically considered for individuals with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 40 or a BMI greater than 35 with obesity-related comorbidities, such as type 2 diabetes or hypertension.
What are the Types of Weight Loss Surgery?
a) Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: One of the most commonly performed weight loss surgeries, this procedure involves creating a small pouch at the top of the stomach and bypassing a portion of the small intestine. By restricting the stomach’s capacity and altering the digestive pathway, patients experience both reduced food intake and malabsorption.
b) Sleeve Gastrectomy: In this procedure, a significant portion of the stomach is surgically removed, leaving behind a narrow, sleeve-shaped stomach. The reduced stomach size limits food intake while preserving the normal digestive process.
c) Adjustable Gastric Banding: A silicone band is placed around the upper part of the stomach, creating a smaller pouch that restricts food intake. The band can be adjusted to modify the size of the opening, offering flexibility for individual needs.
d) Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch: This procedure involves a two-step process. First, a sleeve gastrectomy is performed, reducing stomach size. Then, the surgeon redirects food to bypass a significant portion of the small intestine, leading to reduced calorie absorption.
What are the Short-Term Results of Weight Loss Surgery?
Weight loss surgery has shown remarkable short-term outcomes, often leading to significant weight loss and improvements in comorbidities. Studies have indicated that patients can achieve substantial weight loss within the first 6 to 12 months post-surgery. For instance, one study found that patients undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass achieved an average excess weight loss of 60-80% at one year after surgery.
What are the Hormonal Changes that Occur from Weight Loss Surgery?
Weight loss surgery exerts profound effects on hormonal regulation, which contribute to the observed improvements in metabolic health. For instance, gastric bypass surgery has been shown to alter the production and release of hormones such as ghrelin, which stimulates appetite, and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and peptide YY (PYY), which promote satiety. These hormonal changes play a crucial role in reducing appetite, enhancing satiety, and improving glucose homeostasis.
What are the Long-Term Results of Weight Loss Surgery?
Weight loss surgery has demonstrated significant long-term benefits, extending beyond initial weight loss. Research has shown sustained weight loss and improvements in obesity-related comorbidities in the years following surgery. While individual outcomes may vary, studies have highlighted the following long-term results:
a) Sustained Weight Loss: Long-term studies have indicated that weight loss surgery can lead to sustained weight loss over several years. For instance, a study published in JAMA Surgery followed patients who underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and found that they maintained an average excess weight loss of 55-60%. Another study published in the New England Journal of Medicine reported that patients who underwent sleeve gastrectomy sustained a mean weight loss of approximately 25-30% over five years. However, there are very large variations and many patients regained all of the weight, and then some.
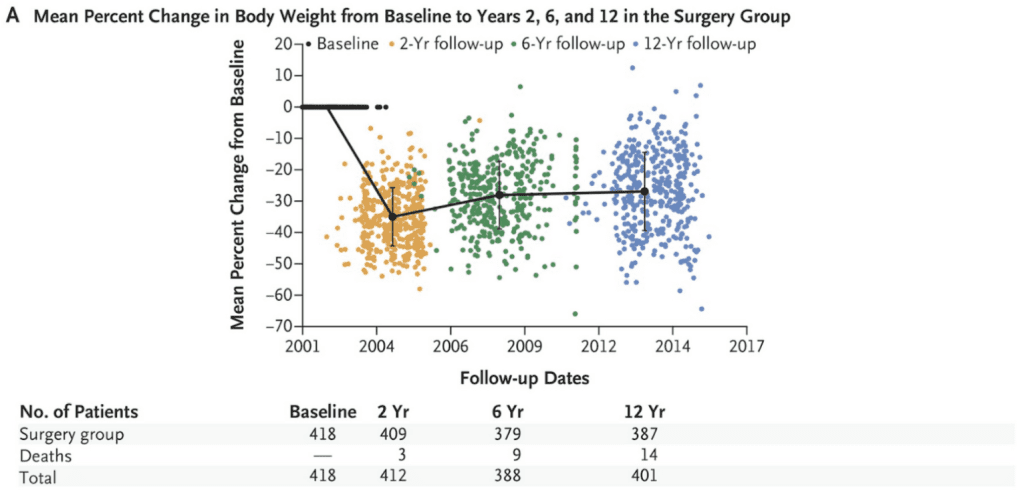
b) Resolution of Comorbidities: Weight loss surgery has been associated with substantial improvements or resolution of obesity-related comorbidities. Conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease have shown significant improvement following surgery. A study published in Diabetes Care reported that Roux-en-Y gastric bypass resulted in at least temporary remission of type 2 diabetes in around 60-80% of patients.
c) Enhanced Quality of Life: Beyond weight loss and medical improvements, weight loss surgery has been linked to an enhanced quality of life. Patients often experience improvements in physical function, mental well-being, self-esteem, and social interactions. A study published in JAMA Surgery found that individuals who underwent weight loss surgery reported substantial improvements in overall quality of life, body image, and self-esteem compared to those who pursued non-surgical weight loss methods.
d) Long-Term Maintenance Challenges: While weight loss surgery can produce significant and sustained results, it is important to recognize the challenges associated with long-term maintenance. Some individuals may experience weight regain or encounter difficulties in adhering to lifestyle changes over time. Ongoing support, follow-up care, and engagement in healthy habits are crucial for maintaining long-term success.
How Lifestyle Changes Help Ensure Weight Loss Surgery Success:
While weight loss surgery can provide a powerful jumpstart to weight loss, long-term success relies on making sustainable lifestyle changes. These changes include adopting a balanced, nutrient-dense diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and addressing psychological factors through counseling or support groups.
A study published in the Journal of Obesity reported that patients who incorporated lifestyle changes, such as increased physical activity and improved dietary habits, had better long-term weight loss maintenance and overall well-being.
Conclusion:
Weight loss surgery offers a path to profound transformation for individuals grappling with severe obesity. Through its various surgical techniques, weight loss surgery reduces food intake, alters hormonal regulation, and jumpstarts weight loss.
While further research is needed to refine surgical techniques and optimize outcomes, weight loss surgery remains a remarkable tool in the battle against obesity, providing hope and improved quality of life for many individuals.
Weight loss surgery offers not only short-term benefits but also long-term results in terms of sustained weight loss, improvements in obesity-related comorbidities, and enhanced quality of life. However, to maximize long-term success, people should embrace comprehensive lifestyle changes that encompass dietary modifications, regular exercise, and psychological support.
While challenges may arise in long-term maintenance, continued commitment to lifestyle changes, regular follow-up with healthcare professionals, and access to support systems can help individuals navigate these obstacles and enjoy the full benefits of weight loss surgery.
Try our nutrition coaching, for free!
Be the next success story. Over 30,000 have trusted Macros Inc to transform their health.
Simply fill out the form below to start your 14-day risk-free journey. Let's achieve your goals together!


