If you’ve ever wondered what people mean when they talk about “counting macros” or if you’re curious about nutrition and want to make sense of how different foods fuel your body, you’re in the right place. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about macros and the macro diet – including what they are, why they matter, and how to use them to create a balanced diet tailored to your goals. From understanding proteins, carbs, fats, and even alcohol, to learning how the macro diet can help you enjoy food without restriction.
Whether your goal is weight loss, muscle gain, or simply eating more mindfully, mastering your macros is a powerful tool for success.
Jump to a Topic
Everything You Need To Know About Macros and the Macro Diet
What Are Macros?
The term “macros” is short for “macronutrients”- a fancy term for the nutrients we need in large amounts to fuel our bodies. Every time you eat, regardless of what kind, you consume macronutrients, which provide the energy your body needs to function, move, and thrive.
There are three main macronutrients and one “honorary” member. The three main ones are:
- Protein
- Carbohydrates
- Fats
The honorary one is alcohol. We call it an honorary one because it isn’t technically a nutrient since it doesn’t provide any “nutrition” to the body, but it does provide calories, so we treat it like a macronutrient in terms of energy intake.
Each macronutrient provides energy, but they are not all the same. Here is how much energy each provides:
- Protein: 4 kcals per gram
- Carbohydrates: 4 kcals per gram
- Fats: 9 kcals per gram
- Alcohol: 7 kcals per gram

Now, let’s take a look at the role of each macronutrient.
Protein: The Building Block
Protein is often the first macronutrient discussed because it plays a unique role in the body and is the one many people struggle to get enough of in their diet. It has distinct functions and is essential for many bodily processes, including:
- Building and repairing muscles
- Producing hormones like insulin and growth hormone
- Repairing tissues (including muscle, connective tissue, and bones)
- Transporting vitamins and minerals throughout the body
Complete vs. Incomplete Proteins
Proteins are made up of amino acids, the building blocks your body needs. There are 20 amino acids in total, and they form the basis of the food we eat. Some amino acids are “non-essential” (your body can make them), while others are “essential” and must come from food.
- Complete proteins (found in animal products like meat, eggs, and dairy) contain all nine essential amino acids.
- Incomplete proteins (found in plant-based foods like beans, rice, and vegetables) lack one or more of the essential amino acids and need to be combined to create a full profile of amino acids.

If you’re eating mostly plant-based or following a vegan diet, it’s important to pair different foods to get all the essential amino acids your body needs. For example, combining legumes with seeds creates a more complete protein than eating legumes on their own.

How Much Protein Do You Need?
The amount of protein needed varies depending on your goals and activity level.
- Minimum Intake: 0.8 grams per kg of body weight (about 0.4 grams per lb)
- Optimal Intake for muscle health: 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kg (0.7 to 1.0 grams per lb)

Carbohydrates: The Body’s Primary Fuel
Carbohydrates serve as one of the body’s two primary forms of stored energy, but they are stored in much smaller quantities than fats. Carbs are primarily stored in the liver and muscle tissues and are constantly circulating in the blood as glucose, providing fuel for our body.
Simple vs. Complex Carbs
Carbohydrates are often classified as either simple or complex based on their chemical structure:
- Simple carbohydrates are made of one or two sugar molecules and provide quick energy. Examples include fruits and table sugar.
- Complex carbohydrates consist of long chains of sugar molecules, which take longer to break down, providing a more stable and sustained release of energy. Examples include whole grains, starchy vegetables, and legumes.
Interestingly, carbohydrates like starch and fiber are both complex carbs made from glucose, but the human body treats them differently. While starch is digested and absorbed for energy, fiber is not, and it passes through the digestive system undigested.
How Many Carbs Do You Need?
Unlike protein, carbohydrate needs depend on total calorie intake and physical activity level. Active individuals who engage in intense or prolonged exercise need more carbohydrates for fuel. The recommended intake varies widely, but generally, you’ll want to aim for between 0.5 grams to 4.0 grams of carbohydrates per pound of body weight.
Fats: Essential and Often Misunderstood
Fat is the most energy dense macronutrient, containing 9 calories per gram. This means that per gram of food consumed, fats contain more than twice the calories of either carbohydrates or protein. Fats are found in our diet through butter, oils, nuts, and seeds, with most of the fats coming from industrialized oils such as canola oil, soybean oil, palm oil, and peanut oil. play an important role in the body by supporting hormone production, vitamin absorption, and brain health. There are 4 different types of fats, and while some are beneficial, others should be limited.
Types of Fats
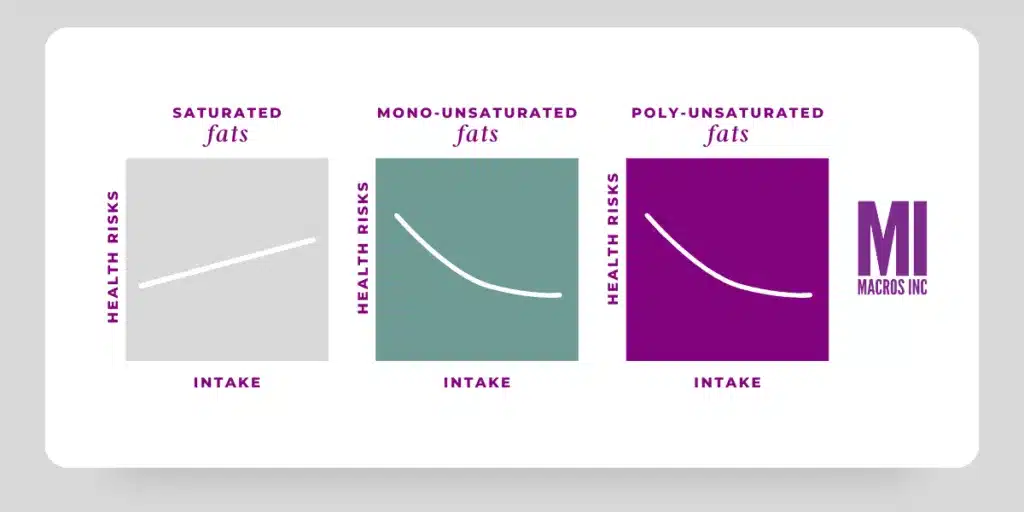
Trans Fats: These are artificially created fats found in processed foods like margarine and some packaged snacks. Trans fats are considered unhealthy and should be avoided as much as possible. The FDA recently put industrial-made trans-fats on the “general not recognized as safe list”. These fats are created from partially hydrogenated oils and it can increase your chances of unfavorable health effects.
Saturated Fats: Found in animal products (like meat, dairy, and eggs), saturated fats have been controversial in the past. While some research suggests they can contribute to heart disease, newer studies show that they might not be as harmful as once thought. It’s best to consume them in moderation (less than 10% of total calories).
Monounsaturated Fats: These fats, found in olives, avocados, nuts and seeds, are considered beneficial for heart health and are a great addition to any diet.
Polyunsaturated Fats: These include omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which are essential fats that the body cannot make on its own. Found in foods like fatty fish, flax seeds, walnuts, and certain vegetable oils e.g. olive oil and canola. These fats, specifically fats known as EPA and DHA, are considered health-promoting and can have positive effects on overall health.
Alcohol: The Honorary Macronutrient
Alcohol is considered an honorary macronutrient because it provides calories (7 kcal per gram), but unlike the other macronutrients, it is not essential for human health. The body cannot store alcohol, and when consumed, alcohol is burned as energy first before the body processes other macronutrients like protein, carbs, and fats.
When alcohol is consumed in excess, it can disrupt metabolism and reduce the body’s ability to utilize stored fat for energy, which is why it’s important to be mindful of how alcohol fits into your overall macro diet. Balance is key. For more information on alcohol and how to track it, you can read more here.
So, we now know what the four macronutrients are, but what is a macro diet?
What is the Macro Diet?
The macro diet is a flexible, science-backed approach that goes beyond counting calories by focusing on the balance of macronutrients – protein, carbs, and fats – because not all calories are created equal. Unlike restrictive diets that cut out certain foods, the macro diet tailors your intake to your specific goals, whether that’s weight loss, muscle gain, or overall wellness.
With this approach, you can enjoy a variety of foods while hitting your personalized macro targets. Using a calculator, you’ll determine the right balance based on your activity level, health goals, and personal preferences. This allows you to eat what you love without feeling deprived, as long as it fits within your daily macros.
The real beauty of the macro diet is its flexibility. There are no rigid rules or ‘off-limit’ foods – you simply focus on balance and moderation. It’s a sustainable way to take control of your nutrition, empowering you to fuel your body in a way that fits your life, and supports both your health and happiness.
Benefits of the Macro Diet
The macro diet isn’t just about tracking numbers – it’s a flexible, sustainable approach to eating that helps you achieve your health and fitness goals. Let’s dive into the key benefits that make this diet so effective:
- Flexibility in Food Choices: Unlike restrictive diets that ban or demonize certain foods, the macro diet focuses on balance and moderation. You can enjoy your favorite treats as long as they fit within your daily macro targets.
- Customizable to Your Goals: Whether you want to lose fat, build muscle, or maintain your weight, the macro diet can be tailored to meet your specific needs and shift as your goals evolve, keeping the diet adaptable over time.
- Precision and Control: Tracking macros gives you a more accurate understanding of your diet and how it affects your body. Using our food-tracking app Macro Sync helps you hit your targets by ensuring you get the right balance of macronutrients to support your goals and maintain calorie control – without the guesswork.
- Education and Awareness: One of the biggest benefits of the macro diet is gaining valuable insight into how food impacts your body. You’ll develop a better understanding of nutrition, portion sizes, and how to identify foods rich in protein, carbs, and fats. The macro diet also encourages mindful eating, helping you build confidence in making healthy choices – even without tracking every meal. It’s a skill that you can carry with you for life, long after you’ve reached your goals, making it more than just a diet – it’s a lifestyle.
- Supports Overall Health: The macro diet helps promote overall well-being by ensuring a balanced intake of protein, carbs, and fats. This balance supports hormone regulation, bone and muscle health, and even blood sugar control. Many who follow this diet see improved digestion, better sleep, increased energy, and an overall boost in mood.

Drawbacks of the Macro Diet
As with most things in life, the macro diet does have its challenges.
- Learning the Ropes: Understanding and calculating the right macros can feel confusing at first. Using our calculator and the Macro Sync food-tracking app can help, but there’s still a learning curve when it comes to balancing meals and getting to grips with tracking.
- Time-Consuming: Weighing and tracking every meal, and ensuring you hit your macro targets can feel tedious and overwhelming to start, especially if you’re new to the process. However, it’s all about progress, not perfection. By breaking things down into manageable steps, you can build your confidence as you go.
- Potential for Miscalculations: Even small inaccuracies – those small licks, bites, and nibbles – can all add up and potentially stall progress. The macro diet does require a level of precision that may not suit everyone, but there are plenty of workarounds.
- Social Challenges: Eating out or attending social events can be a bit tricky, as it’s harder to control or estimate your macros in restaurants or meals prepared by others. This may lead to feelings of restriction in social situations.
However, all of these challenges can be overcome with practice, planning, and a balanced mindset. We also have tons of free, helpful guides packed with tips and practical advice. If you need extra support, our nutrition coaching will give you the tools to navigate these situations and achieve lasting results.

Wrap Up
The macro diet is more than just a way of eating – it’s a flexible, personalized approach to fueling your body that puts you in control. By focusing on balance, understanding your macronutrient needs, and making mindful food choices, you can achieve your health and fitness goals without feeling restricted.
While the journey may have its challenges, the tools and skills you gain along the way are invaluable. Mastering your macros is a sustainable strategy that empowers you to enjoy food, stay on track, and live a balanced life.
Ready to take the next step? With the right support and resources, you can confidently navigate the macro diet and make it work for you – no matter your goals.
Try our nutrition coaching, for free!
Be the next success story. Over 30,000 have trusted Macros Inc to transform their health.
Simply fill out the form below to start your 14-day risk-free journey. Let's achieve your goals together!

