Most diets that have been used with great success over the last several decades have one thing in common: they all acknowledge that protein is a critical part of losing weight and maintaining or increasing lean muscle mass.
Regardless of whether it is a plant-based vegan diet, an all-meat carnivore diet, or something completely different, they almost all agree that protein is important in your diet.
This article is going to cover why protein is important in your diet, especially if you are looking to lose weight and/or build muscle.
Understanding Protein
To develop an understanding of the importance of protein in your diet, it is essential to understand how it differs from other macronutrients.
Protein
Proteins are composed of amino acids and are the building blocks of cells, tissues, and organs in the body. They play a crucial role in various physiological functions, including growth, repair, and maintenance. Unlike carbohydrates and fats, protein contains nitrogen, which is necessary for the synthesis of new proteins in the body.
Carbs
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. They are made up of sugar molecules and can be classified into two types: simple carbohydrates (such as glucose and fructose) and complex carbohydrates (such as starches and fibers). Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose during digestion, which is then utilized by the body for energy production. They provide readily available energy to fuel various bodily processes.
Fat
Fats are a concentrated source of energy and serve as a vital energy reserve for the body. They are composed of fatty acids and come in different forms, such as saturated fats, unsaturated fats (monounsaturated and polyunsaturated), and trans fats. Fat plays several crucial roles in the body, including providing insulation, protecting organs, facilitating the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, and serving as a structural component of cell membranes.
Protein: An Essential Macronutrient
Additionally, protein is what is known as an essential macronutrient. The term essential in this context means the body has to get protein through the diet, it cannot make protein on its own. Protein is made up of amino acids (AA).
The 9 Essential Amino Acids
There are 20 amino acids in total needed by the human body. This can be broken down into subcategories of essential and nonessential amino acids. There are 9 essential amino acids, meaning the body cannot make those 9 by itself and must consume them in the diet.
The 9 essential amino acids are:
- Leucine
- Isoleucine
- Valine
- Lysine
- Tryptophan
- Threonine
- Methionine
- Phenylalanine
- Histidine
This is important as you’ll need all 9 to regulate many bodily functions. In addition, you’ll need all 9 to maximize muscle retention or muscle growth. This is why animal protein sources are generally superior to plant sources.
They generally yield higher absolute protein amounts as well as possessing all 9 essential amino acids making them a complete protein. Most plant sources are incomplete meaning they lack at least 1 or more of these essential amino acids with some exceptions like soy.
But even when comparing equal amounts of complete protein, animal sources, compared to plant sources, seem to be superior for muscle building.
Why Protein is Important in Your Diet
Consuming enough protein is important not only for weight loss (more on that in a minute) but it is also critical for overall health. Here are a few reasons why adequate protein intake (regardless of everything else) is important:
- Optimal health and bone density.
- Improves sleep quality:
- A high thermic effect of food meaning you’ll burn extra calories from digestion.
- Proper Satiation as you’ll need a baseline of protein to be full. In addition, protein is generally more filling than carbs/fat especially in people who undereat protein.
- Optimal muscle retention/building based on energy balance.
This is why at Macros Inc, we make sure clients eat the correct amount of protein for their needs. It’s arguably the most important macro to optimize to feel great and look your best. It’s not merely a nutrient bodybuilders love to talk about to build muscle.
Why Protein is Important for Muscle Growth
When we think of building muscles, protein immediately comes to mind. It’s no secret that protein plays a pivotal role in muscle development and growth. In this chapter, we will delve into the reasons why protein is of utmost importance for maximizing muscle gains. Let’s uncover the science behind the muscle-building potential of protein.
The Building Blocks of Muscles
As touched on earlier, muscles are composed of proteins, and consuming an adequate amount of protein is essential for providing the building blocks necessary for muscle growth. Proteins consist of amino acids, which act as the primary structural components for repairing and building muscle tissue. By ensuring sufficient protein intake, you supply your body with the necessary amino acids to support muscle growth and recovery.
Protein Synthesis and Muscle Adaptation
Protein synthesis is a crucial process that takes place within our bodies, responsible for repairing damaged muscle fibers and promoting muscle growth. Consuming protein-rich foods or supplements following a workout can significantly enhance protein synthesis, leading to improved muscle adaptation. By providing your muscles with the fuel they need to rebuild and grow, protein plays a key role in optimizing the muscle-building process.
Protein and Strength
Protein and resistance training go hand in hand when it comes to muscle growth. Engaging in regular resistance training exercises creates a stimulus for muscle fibers to adapt and grow. However, without an adequate protein supply, the potential for muscle growth is limited. Combining resistance training with a protein-rich diet creates a synergistic effect, maximizing muscle protein synthesis and fostering significant muscle gains.
Why is Protein Important for Weight Loss?
When it comes to weight loss, protein often takes a backseat to its reputation as a muscle-building nutrient. However, protein is not only important for building lean muscle but also plays a vital role in effective weight loss. In fact, it may be the most essential macronutrient to optimize during your weight loss journey. Let’s explore why protein deserves a prominent place in your weight loss strategy.
Preserving Muscle During Caloric Deficit
When you’re on a diet, you consume fewer calories than you burn, creating a caloric deficit. This deficit can trigger a catabolic state, where your body starts utilizing tissue, including muscle, for energy. But here’s where protein comes to the rescue.
Consuming protein sends an anabolic signal to your body, encouraging it to prioritize muscle preservation even during periods of calorie deficits. By ensuring an adequate protein intake, you can maintain your hard-earned muscle mass while shedding unwanted body fat.
Boosting Caloric Expenditure
Did you know that digesting protein requires more energy compared to digesting carbohydrates and fats? It’s true! This means that your body burns more calories while processing protein-rich foods. So, not only does protein help you build and maintain muscle, but it also gives your metabolism a little boost.
The term “the meat sweats” isn’t just a myth—it reflects the increased calorie expenditure during protein digestion. Moreover, meals that include protein, especially in combination with other nutrients, can further enhance the caloric burn during digestion.
Satiety and Feeling Fullness
If you’ve ever found yourself feeling hungry shortly after a high-carbohydrate or high-fat meal, it’s time to consider incorporating more protein into your diet. Protein has the remarkable ability to promote satiety, keeping you feeling fuller for longer. In fact, most protein sources are more filling than their carbohydrate and fat counterparts.
By including an adequate amount of protein in your meals, you can maximize the sensation of fullness, which can be immensely helpful for weight loss. Those who are new to consuming sufficient protein will experience its satisfying effects firsthand.
Sources of Protein
Here are a list of recommended protein sources that are high in protein while being low in calories: chicken breast, chicken thigh, fish, seafood, turkey, turkey sausage, lean beef (lean cuts w/ round or loin in their names), ground turkey, ground beef (at least 90% lean), pork tenderloin, lean deli meats, egg whites, fat free Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, protein powder (whey or casein is best), game meat, organ meat.
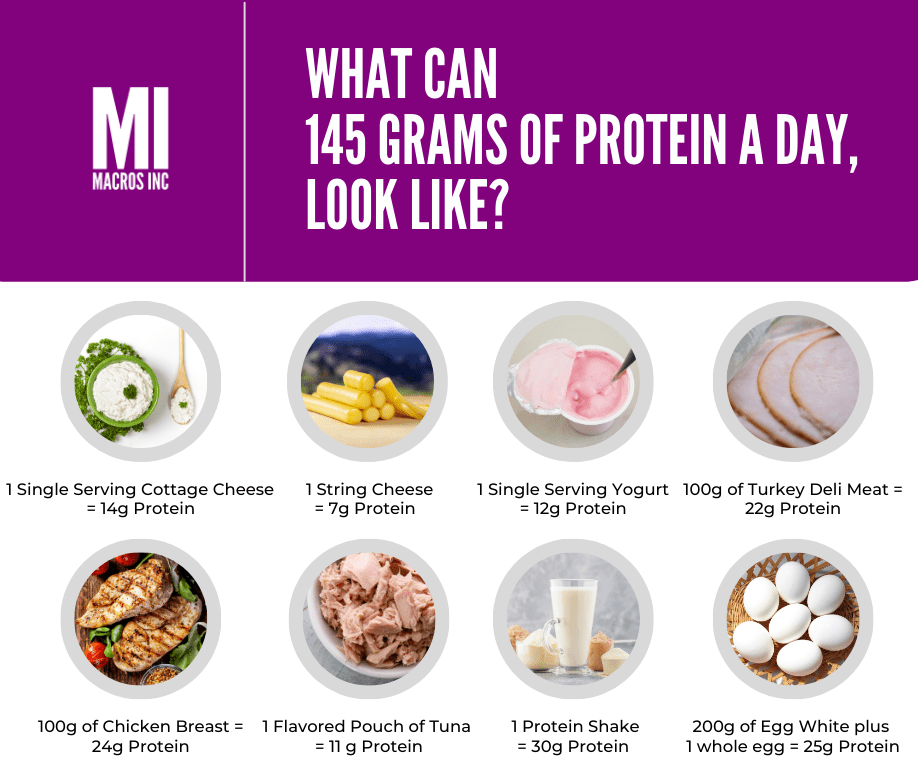
Most people will have to eat one of these sources at every meal or supplement with a protein powder/drink to meet their protein targets.
Protein Supplements
As for protein supplements, the 2 main types are whey and casein, both of which are made from dairy. Minimal lactose is in both, but if intolerance occurs, feel free to use something like egg protein.
As for whey and casein, whey is considered a faster protein meaning it spikes amino acids into the blood quicker, but at a less sustained rate. Casein spikes amino acids weaker, but at a more prolonged rate. Research shows there isn’t much net difference, so don’t fret too much about which one to get.
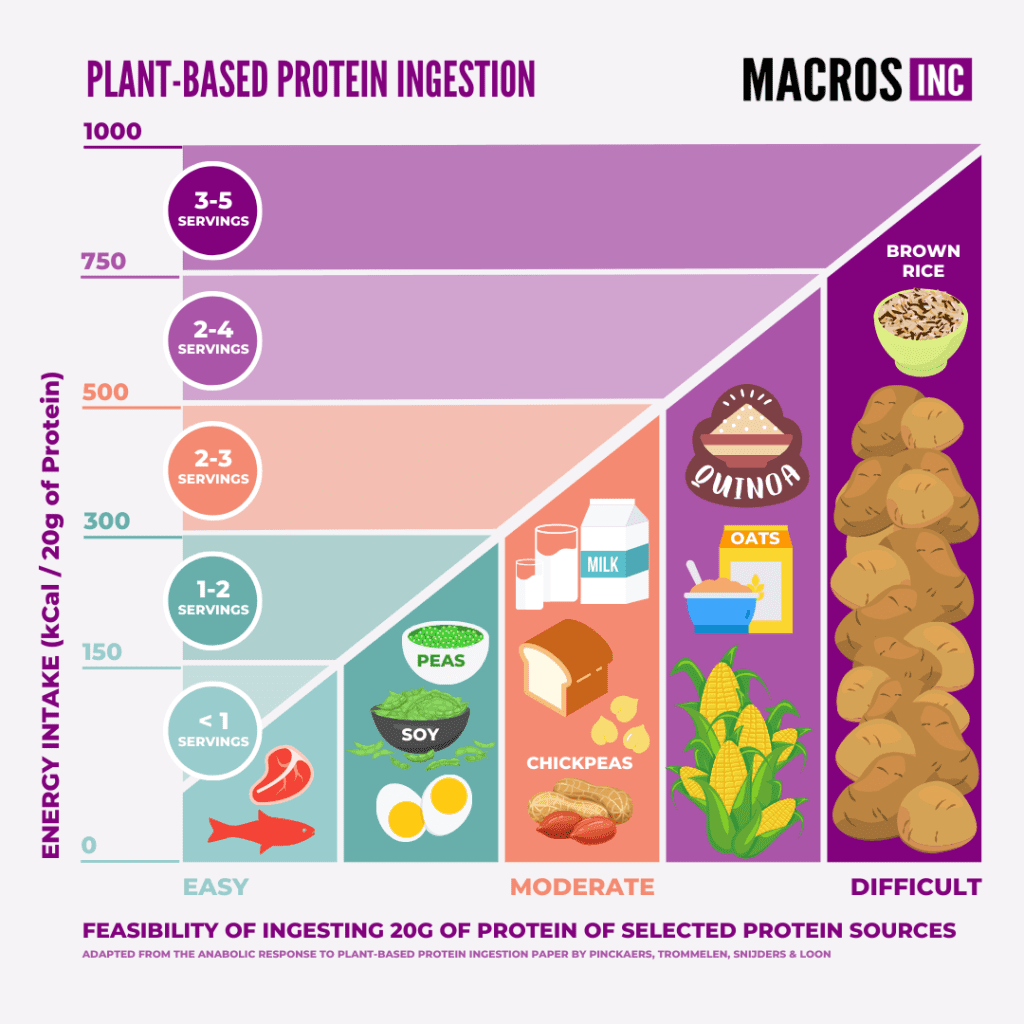
There are also plant based sources of protein that individuals who follow a plant-based diet can utilize. These include foods such as: soy beans, tofu, chickpeas, lentils, quinoa, black beans, nuts and seeds (e.g. almonds and sunflower seeds) also have protein but are very energy dense sources of protein.
There are also plant based protein powders that utilize mixes of plant proteins (such as rice and pea) to create complete amino acid profiles.
To figure out how much protein per day is right for you, use our Macro Calculator.
Summary
Of all three macronutrients, protein is often the one most focused on because it can be the biggest lever you can pull in your diet to affect change in body composition. This is because protein has the greatest effects on lean body mass and satiety of the three macronutrients.
As such, it is often considered the most important macronutrient, especially for people trying to lose weight and/or build muscle.


