For many people, gaining muscle can seem like a mystery. Have you spent years in the gym toiling away, only to make basically no notable progress? Well, you are not alone. There are countless people who spend a lot of hours in the gym trying to gain muscle but can never crack the code.
Today I am going to unlock that code for you using two very simple principles.
Principle 1: You have to put enough stimulus on your muscle to force it to grow.
Principle 2: You have to be eating in a caloric surplus for an extended period of time.
Jump to a Topic
How Do I Gain Muscle?
Training to build muscle is both an art and a science. It is also a little more complicated than weight loss.
Fundamentally you can lose weight doing basically any type of exercise and just eating in a deficit. However, building muscle requires a few key things:
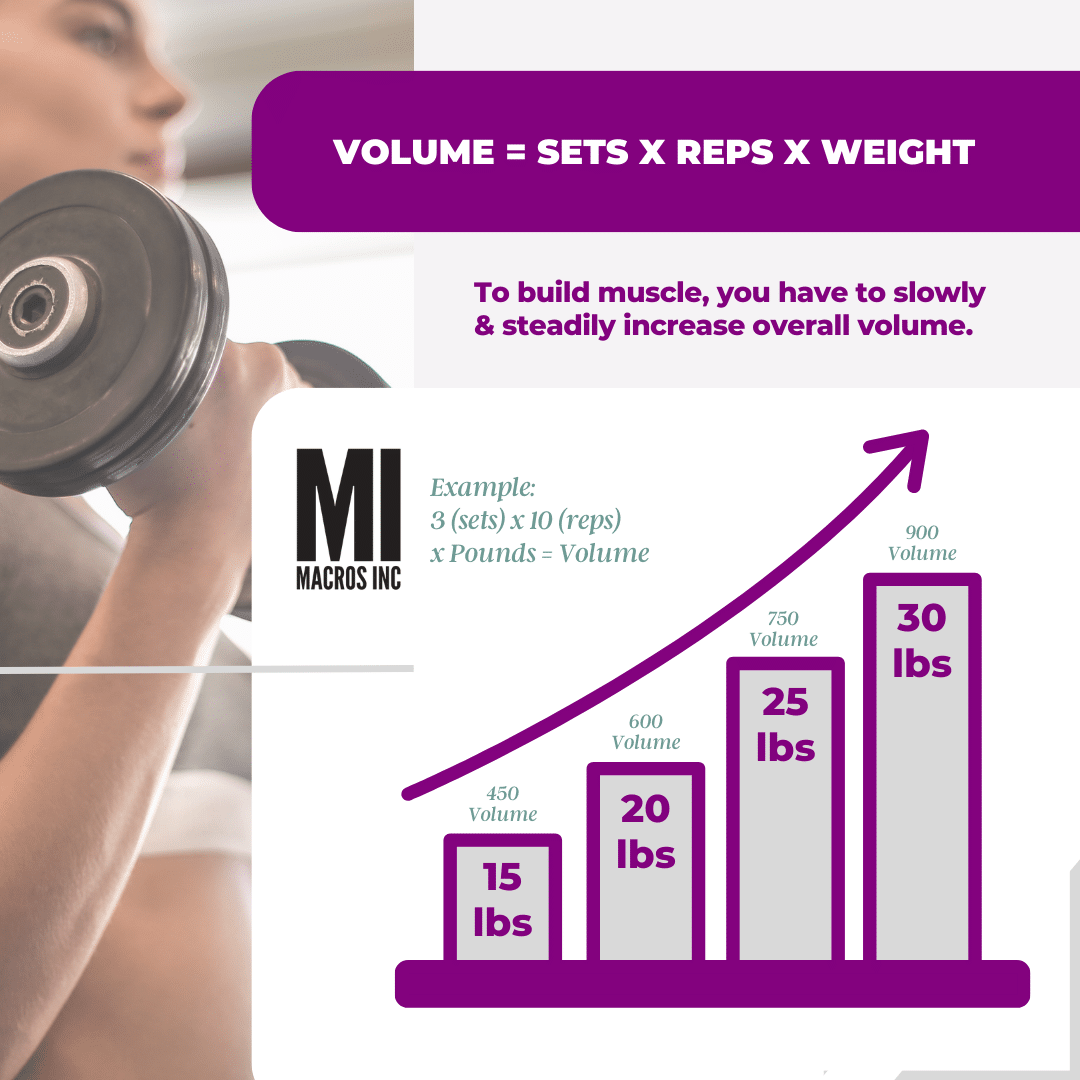
The volume of a workout is determined by three factors: weight, sets, and reps. The equation for counting your volume is relatively straightforward.
You have to slowly and steadily increase the overall volume of your workouts.
It is simply volume=sets x reps x weight
For example, if you did 3 sets of bicep curls for 10 reps with 30 pounds, that exercise would be:
3 (sets) x 10 (reps) x 30 (pounds) = 900.
Now count that up for each exercise. And overtime that number for each training block should be increasing.
It is about the weight on the muscle, not the weight on the bar
One of the fundamental differences between weightlifting/powerlifting, and bodybuilding as a sport is that weightlifting/powerlifting focuses on moving a weight, whereas bodybuilding focuses on moving a muscle.
This seems like a trivial idea, but it is actually everything… like e.v.e.r.y.t.h.i.n.g.
In fact, one of the most iconic quotes in the history of body building was when Kai Greene said, “I am not a weightlifter”
Muscle growth requires mechanical tension on the muscle and the greater the tension, the greater the result. This means that when you train to build muscle you should focus way more on the quality of the rep and the engagement of the muscle during that rep.
Less variety is actually better
One way to ensure you stall your progress building muscle is to change the exercises you do every couple of weeks. The thing about building muscle is that you need a similar stimulus in type but a greater stimulus in magnitude over time to keep growing.
Every time you switch exercises you essentially reset the type of stimulus and the magnitude of the stimulus. The most successful bodybuilders will do the same exercises for months or years before they change them.
Be super consistent in what you do, and be consistent in how well you increase the volume of what you do.
The Benefits of Following a Structured Program
Now that we’ve covered the essential principles of muscle building, it’s crucial to understand the advantages of following a structured program. While the concepts discussed above are foundational, a well-structured program provides the framework necessary to put these principles into action effectively.
Here’s why adhering to a structured program can significantly benefit your muscle-building journey:
1. Progressive Overload Made Simple: A structured program provides a clear roadmap for progressive overload – a fundamental element in muscle growth. By outlining the sets, reps, and weights to use over time, it eliminates the guesswork. You can track your progress and make gradual increases in volume without the confusion of constantly changing variables.
2. Consistency and Tracking: Consistency is key when it comes to building muscle. A structured program helps you stay consistent by specifying which exercises to perform and how to perform them. This consistency aids in tracking your improvements and ensuring you stay on the right path toward your muscle-building goals.
3. Avoiding Plateaus: As mentioned earlier, constantly changing exercises can lead to plateaus in muscle growth. Structured programs emphasize the importance of sticking with specific exercises for extended periods. This approach ensures that you maintain the necessary stimulus and continue to challenge your muscles for growth.
4. Focused Muscle Engagement: Following a structured program encourages you to concentrate on the quality of each repetition and the engagement of the targeted muscle group. By providing clear guidelines, it reminds you to prioritize muscle contraction over simply moving weights. This meticulous focus can lead to more efficient muscle development.
5. Long-Term Progression: Building muscle is not a short-term endeavor. It requires consistent effort and patience. Structured programs often span 12 weeks or more, aligning with the long-term nature of muscle growth. By following such a program, you commit to a sustainable approach that allows you to see substantial results over time.
Strength Training Programs
Here are two comprehensive workout guides that can help you to maximize the results from training:
6-Day PPL Workout Guide:
Our 6-Day PPL (Push, Pull, Legs) workout plan is designed for intermediate to advanced fitness enthusiasts. It spans 12 weeks and focuses on specific muscle groups on designated training days, ensuring maximum efficiency and recovery.
Key Details:
- Equipment Required: Barbell, Dumbbells, Machines
- Program Duration: 12 weeks
- Time per Workout: 45-60 minutes
- PPL Breakdown: The 6-Day PPL program is organized into Push, Pull, and Leg days.
- Push Day: Focuses on chest, shoulders, and triceps.
- Pull Day: Targets back, traps, and biceps.
- Leg Day: Strengthens quads, hamstrings, and calves.
4-Day PHUL Workout Guide:
Our 4-Day PHUL (Power Hypertrophy Upper Lower) program spans 12 weeks, providing ample time for your body to adapt and grow. It balances power and hypertrophy for a well-rounded workout experience.
Key Features:
- Equipment Needed: Barbell, Dumbbells, Machines
- Days Per Week: 4
- Workout Duration: Each session takes 45-60 minutes.
- Workout Split: The PHUL plan is divided into four workout days, each focusing on power or hypertrophy.
Power Day – Upper Body (Day 1):
- Focuses on building upper body strength.
- Includes exercises like Bench Press, Barbell Row, Incline Press, Lat Pull Down, Overhead Press, Bicep Curl, and Skullcrushers.
Power Day – Lower Body (Day 2):
- Targets lower body power and development.
- Comprises exercises such as Squat, Deadlift, Leg Press, Leg Curl, and Standing Calf Raise.
Hypertrophy Day – Upper Body (Day 3):
- Concentrates on upper body muscle growth.
- Incorporates Incline Bench Press, Seated Cable Row, Dumbbell Chest Fly, Dumbbell Row, and Dumbbell Lateral Raise.
Hypertrophy Day – Lower Body (Day 4):
- Aims to enhance lower body size and definition.
- Includes Squat, Bulgarian Split Squat, Leg Press, Leg Curl, and Leg Extension.
Download our 6-Day PPL Workout Plan, here.
Download our 4-Day PHUL Workout Plan, here.
Wrap Up
Building muscle is a process that relies on principles such as progressive overload, consistent training, and focused muscle engagement. Understanding the importance of volume in your workouts and emphasizing the quality of repetitions over simply moving weights are key factors in muscle growth.
Moreover, avoiding excessive exercise variety and adhering to a structured program can significantly enhance your muscle-building journey. These structured programs, like the 6-Day PPL and 4-Day PHUL workout guides, provide clear roadmaps for your training, promote consistency, prevent plateaus, and ensure long-term progression towards your muscle-building goals.
By incorporating these principles and programs into your fitness routine, you can optimize your efforts and achieve the muscle development you desire.
Try our nutrition coaching, for free!
Be the next success story. Over 30,000 have trusted Macros Inc to transform their health.
Simply fill out the form below to start your 14-day risk-free journey. Let's achieve your goals together!


